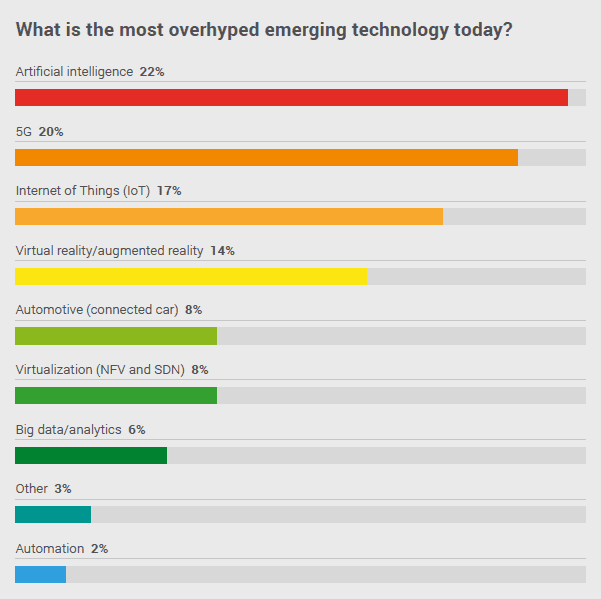
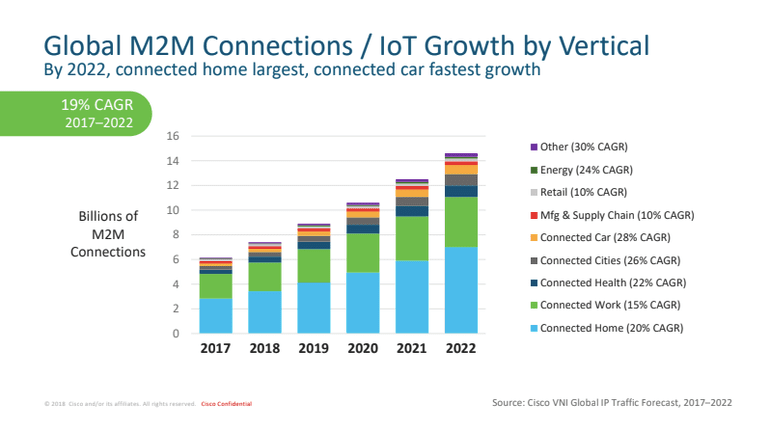
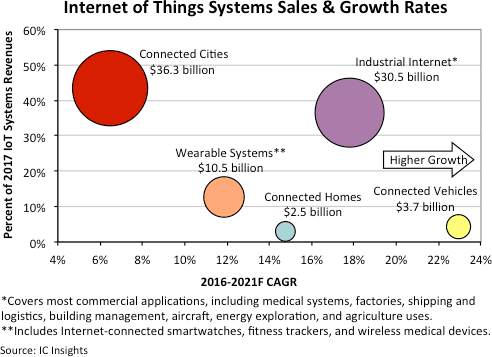
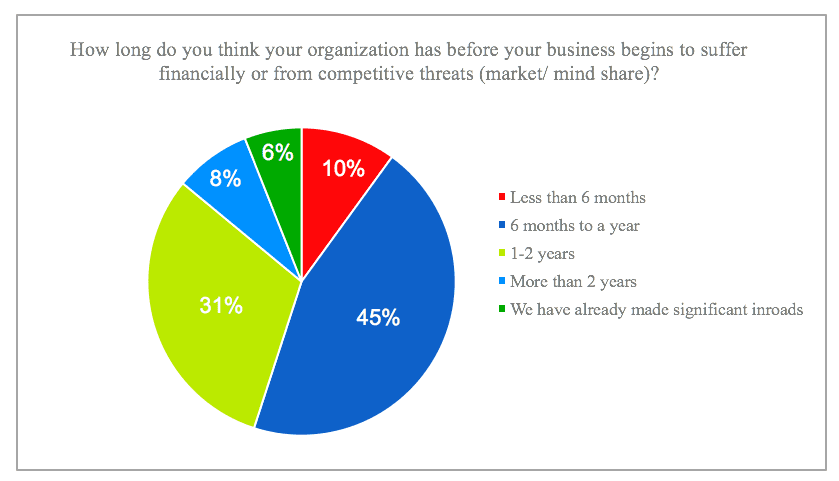
Internet of Things and beyond... simply...and for everyone.
Do you wonder about what the Internet of Things (IoT) is all about?
Are you looking to expand your understanding of IoT with real life examples?
Would you like to better understand the impact of the 4th industrial revolution?
Jeff Travers, Head of IoT Connectivity Management, Ericsson “All industries will continue to explore how Industry 4.0 can help their bottom lines and new and compelling use cases will emerge. One area well positioned to benefit from technologies such as augmented reality (AR) is field services. Experienced engineers are hard to find and those they do have can only visit so many remote sites in a year. Enabled by 5G and the speed with which data can travel through the air, AR will enable engineers-in-training to be able to have instant intelligence about a device on which they may be working just by pointing their tablet towards it. This will allow them to rely less on sheer experience and intuition but still be able to make informed decisions. Seasoned engineers will be empowered to accomplish more in less time with access to that same, instant insight provided by AR applications and powered by 5G.”
Warren Chaisatien, Global Director of IoT Customer Engagement Marketing, Ericsson “In 2019, we will see more widespread deployment of 5G networks, which will directly result in the emergence of new and interesting use cases for the technologies associated with Industry 4.0—AR/VR, autonomous cars, AI/ML and IoT. All of these technologies will be dependent upon greater access to 5G technology, which is well suited to support the diverse, but demanding needs of the likes of IoT and AR/VR. 5G will enhance the capabilities of edge computing, which will be particularly vital to certain technologies, like self-driving cars, where computing must be performed as close to the device as possible to reduce the latency of decision making. The list of emerging technologies ready to cut the cord and take their capabilities to the next level when 5G finally becomes available in 2019 is long. In addition to those previously discussed, other include robots, drones, manufacturing, public safety/emergency, and government services. Telecom providers will begin evolving into connectivity managers. Telecom operators will evolve from simply network providers to connectivity managers. In 2018, telecom operators provided the fundamental needs—network access. Going forward, we will see many of them move to the next level, offering enterprises the ability to manage their field of connected devices, and not just connecting those devices, but managing their entire lifecycle.”
Jamie Bennett, VP of Engineering, Canonical “5G has been promised for 2019, but in reality, this is years away. What we’re going to see being rolled out can be defined as an enhanced 4G hybrid model. However, with the current fixed networks, 5G is not yet essential. Once industries scale up and begin adopting edge computing, it will become crucial to add a 5G fast lane for better connectivity.”
Keith Pennachio, Executive Vice President, SQUAN “In every single scenario, the data collected from IoT devices is only as reliable as the robustness of the network to which they are connected. Funding from non-telco entities like Facebook, Apple, and Google, for example, will likely make its way into the telecom infrastructure sector. Additionally, I expect to see a greater rationalization of P3 arrangements across Network Operators, Government Entities, Real Estate Developers, and Utilities.”
Bruce Chatterly, CEO, Senet “2019 will see two major trends that will feed off of each other and propel the Internet of Things to its next stage of growth. First, Tier 1 carriers, cable operators and MVNOs will move beyond their evaluation and small regional deployments of Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWANs) and begin providing national and global connectivity plans. Innovative LPWAN network deployment and ecosystem engagement models will facilitate rapid network expansion and drive change in traditional networking architectures. Second and simultaneously, first-mover markets like water and gas metering will begin deploying connected devices at scale. The “proof-of-concept” in these markets will be replaced with large-scale commercial deployments, creating the foundational proof points other markets are seeking to justify their IoT technology choice and go-to-market strategies.”
Cybersecurity Industry Insight
Hansang Bae, CTO, Riverbed Technologies “IoT hasn’t been overhyped, but it is underdeveloped. The widespread and rapid adoption of IoT devices has caused manufacturers to fast-track development, sacrificing the advanced security technologies that would provide greater protection in favor of low production costs. This will lead to widespread IoT security breaches in 2019. These breaches will be large enough and damaging enough to create a shift in attitude about IoT across the spectrum of end-users, developers and device manufacturers. First, there will be a wake-up call and the realization that there is no quick fix to the security breaches – only smart security investments and re-engineered devices. As developers begin to prioritize security over ease of access, we’ll see a slowdown in the development and adoption of IoT devices, which will ultimately lead to the long-term success of the technology. These breaches—and the search for their solutions—will also boost other technologies, such as machine learning.”
Chris Rouland, Founder and CEO, Phosphorus “Despite all the obvious warning signs, IoT security will NOT tighten in 2019. The race is on to automate just about everything and, unfortunately, security is an afterthought, resulting in glaring vulnerabilities just waiting to be exposed. It’s 1988 all over again as we enter the Robert Morris era of IoT security, and it will likely take a devastating attack on a massive scale before IoT security becomes a top priority and receives the attention it deserves.”
Andrew Howard, CTO, Kudelski Security “Cyber and IT systems will continue to interface closer with IoT and OT environments, enabling new lines of business and greater efficiency, but also opening organizations to new lines of attack. IoT will continue to be a compelling proposition to build a connected culture (smart cities, smart homes, etc.), however leading to increased attack surfaces and increased privacy and security concerns in general. The complexity of the IoT ecosystem will continue to drive security vendors to research and develop products around IoT visibility, monitoring, and management (IoT Edge computing/platforms to evolve and grow). As the proliferation of IoT devices continues, we will see attack services and hacking tools on the rise, with automation as a trend for malware too. In 2019 IoT botnet exploitation will intensify, with industrial IoT as the primary target. Cybercriminals will take advantage of IoT as a platform and blockchain based command-and-control for botnets. This will likely increase the cost of controls and compliance as well as spur new regulations that will mandate critical infrastructure industry to disclose cyber-attacks and hold companies accountable. With the increasing threats, industries such as supply chain will begin to place greater demands on their suppliers for security certifications and audit reporting. This will in-turn mandate suppliers to develop [a] security-by-design product.”
George Kamis, CTO for Global Governments and Critical Infrastructure, Forcepoint “Networked industrial control systems (ICS) that require “always-on” connectivity represent an expanded attack surface, and nowhere is that more apparent than in IoT devices. WiFi and other network-connected sensors in autonomous vehicles and appliances have introduced a rapidly evolving set of security requirements. While attacks on consumer IoT are prevalent, the possibility of disruption in manufacturing and similar industries makes the threat all the more serious. In 2019, attackers will break into industrial IoT devices by attacking the underlying cloud infrastructure. This target is more desirable for an attacker— access to the underlying systems of these multi-tenanted, multi-customer environments represents a much bigger payday. There are three issues at play: the increasing network connectivity to edge computing; the difficulty in securing devices as more compute moves out to the edge, as they do in remote facilities and IoT devices, and the exponential number of devices connecting to the cloud for updates and maintenance. As control systems continue to evolve, they will be patched, maintained, and managed via cloud service providers. These cloud service providers rely on shared infrastructure, platforms, and applications in order to deliver scalable services to IoT systems. The underlying components of the infrastructure may not offer strong enough isolation for a multi-tenant architecture or multi-customer applications, which can lead to shared technology vulnerabilities. In the case of industrial IoT, a compromise of back-end servers will inevitably cause widespread service outages and bring vital systems to a screeching halt. Manufacturing, energy production, and other vital sectors could be affected simultaneously. With Meltdown and Spectre in 2018, we saw vulnerabilities that bypass the software and firmware layers to expose processor hardware to exploits. In this scenario, attackers use low-privilege programs in order to access more critical data, such as private files or passwords. Almost all CPUs since 1995 are thought to be vulnerable, and new variants of Spectre continue to surface. Attackers will divert their attention on developing variants that subvert the underlying cloud infrastructure used by IIoT systems. As processor speed is critical to performance, manufacturers and cloud service providers could continue to choose speed over security in order to gain a competitive edge, inadvertently introducing further vulnerabilities. Organizations will need to move from visibility to control where the IT and OT networks converge to protect against these deliberate, targeted attacks on IIoT systems.”
Pedro Abreu, CSO, ForeScout Technologies “Malicious actors will leverage Buildings Automation Systems (BAS) in a major public ransomware attack. Building automation systems and other advances in technology are driving the rapid adoption of smart buildings. Making a building intelligent can offer numerous benefits and savings, but also introduces new risk and as adoption continues, we will see not just an increase in the volume of malicious activity, but an increase in the severity and damages.”
Scott Nelson, Chief Product Officer, Digi International “Since blockchain hit the public consciousness with the growth of cryptocurrencies, its other potential applications have been a constant topic of conversation. Those will turn into a practical reality as IoT developers have gathered the expertise needed to deploy blockchain for IoT device security needs. While secure data transportation, e.g. patient health records, and automated contracting, e.g. logistics transactions will remain an area of focus for institutions, device manufacturers will find blockchain addressing access and authorization needs. These early IoT adopters will use blockchain to control access to both devices and networks. They will remove and grant access through integrated device members of chain including smartphones. The blockchain offers to remove the opposition of security and usability. As manufacturers retrofit installed equipment with new monitoring and management features secure access will enable deployment and usability will avoid churn.”
Dean Weber, CTO, Mocana “We have begun to see digital transformation projects being held up because they cannot address security. This is an issue because, in order for digital transformation to be successful and use it to make informed decisions based on data analytics and AI, the data needs to be trustworthy. If you can’t trust the device, you can’t trust the data to make smart decisions or else it will disrupt operations or make other costly impacts. If the device is compromised, the data will be compromised as well. We call this “garbage in and garbage out”. This will make organizations look at devices with security built in instead of bolted on in 2019. Silver Bullets Don’t Exist. In 2018, we saw a lot of leadership adopt technologies due to their hype and false pretenses that they would be the quick and easy fix for their organizations’ risks. Blockchain is a great example of one of these technologies. This is one of the biggest areas that we have seen leadership make mistakes.”
Derek Jose, co-founder and CPO, Flutura Decision Sciences and Analytics "One of the primary challenges in the practical execution of IoT projects is blind spots in vital signals. Making assets and process context-aware requires heightening the assets’ sensitivity to events both within them (quality of lube oil, sound anomalies etc.) and around them (Sulphur gas emissions, pressure). The quality of models is directly correlated to the quality of sensor streams. The better sensors get, the better the AI/IoT models become. Second, dedicated IoT sensor data ‘highways’ will form a backbone for industrial companies. Today’s data networks are insufficient to keep up with high data transmission rates required by rising sensor density on upstream/downstream processes/assets combined with the increased frequency of transmission. Companies like Sigfox and Ingenu are focused on building dedicated next-generation sensor data transmission infrastructure for moving sensor data at scale from point A to point B. It’s like getting a dedicated lane on the national highways where you can move sensor data streams – vibration, pressure, sensors, rpm etc without sharing the ‘data lane’ with consumer data to support machine critical upstream, midstream, and downstream processes and the equipment powering these processes.”
Sastry Malladi, CTO, FogHorn “Hybrid- and multi-cloud solutions will dominate the industrial IIoT deployments. As industrial organizations look to bring multi-cloud environments tog provide a more cost-effective approach and flexibility, it will be important for edge solutions to be cloud agnostic. Vendor-exclusive solutions will likely begin to fall by the wayside as companies look for more flexibility and freedom of choice when building their edge-to-cloud environments. Google, AWS, Microsoft, C3IoT, Uptake, and other leading cloud providers will establish more collaborative partnerships with edge computing companies to help businesses as they continue to improve and expand their offerings.”
Alan Conboy, Office at CTO, Scale Computing “Next year [2019] will be a defining year for edge and hybrid computing strategies as IoT and the global network of sensors pile on more data than the average cloud has had to handle in the past. This transition will officially crown edge computing as the next big thing. 45 percent of all data created by IoT devices will be stored, processed, analyzed and acted upon close to or at the edge of a network by 2020. In the process, edge computing will take on workloads that struggle on hosted cloud environments, passing the torch over to HCI platforms.”
Bill Peterson, VP of Industry Solutions, MapR “Organizations will save time and money by processing and analyzing data at the edge versus moving it back to a core, storing it and applying traditional analytics. Use cases include anomaly detection (fraud), pattern recognition (predicting failures/maintenance) and persistent streams. Autonomous vehicles, Oil and gas platforms, medical devices are all early examples of this trend that we will see expand in 2019. Cost drivers for this trend are bandwidth (semi-connected environments as well as expensive cellular) considerations and storage (reduce the amount of data sent to the cloud).”
Ashish Syal, Chief Engineer for the IoT, Sierra Wireless “In 2019, the maturation of open source hardware and software platforms built specifically for the IoT will give makers and developers the tools they need to test ideas and cost-effectively build IoT proof of concepts that can be integrated into digital transformation strategies. Industry leaders like Google, AT&T, Orange, and Bosch are investing in maker and developer communities, as they are bellwethers of IoT-enabled digital transformation. The availability of new IoT Device to Cloud (D2C) platforms that simplify and speed the processing, filtering and prioritization of data at the edge, as well as the transfer of data into ERP, CRM, SaaS and other applications, will enable enterprises streamline supply chains, develop new business models and improve customer experiences, creating further IoT-enabled digital transformation strategies. The winning D2C platforms will truly make it easy to deploy IoT applications (beyond the marketing hype). Engaging and growing the IoT developer community will be a key metric to determine the monetization for these IoT D2C platforms.”
Smart Cities Industry Insight
Glenn Lurie, CEO, Synchronoss “We’re going to see a smart city breakthrough in 2019 which will bring with it a wave of services from the connected car to the smart building and more on the smart home. But, these smart applications are connected individually and do not have interoperability, therefore are essentially disconnected from each other—which is a massive missed opportunity for consumers. Although a single platform that would allow for the management of a single connected life experience is not a reality today, and may not be for some time, the smart city will emerge as the umbrella with successful use cases – including smart buildings, connected cars, vehicle-to-vehicle and vehicle-to-infrastructure and smart grids—that demonstrate problem-solving and moving us closer to a truly connected life. Carriers will also move forward to find ways to set up and sell new services, and drive incremental revenue quickly to capitalize on this.”
“For smart cities to gain traction, we need to focus the agenda for smart cities toward smaller use case studies for improving areas like public safety and sustainability. That needs to start with connecting the information inside the built environment to a smart city context. Recently significant advances have been made to connect these built environments with the cities that surround them, particularly with sensors that connect buildings to existing infrastructure. The sharing of information between these smart buildings and smart cities has to happen through a common infrastructure, data standards, and access models, prioritizing interests of citizens and businesses to improve city life and safety. In the near future, smart building technology will integrate with smart city services to save lives by automatically updating first responders on security lockdowns, building fires, and medical emergencies. However, for smart cities to succeed, the deployments should focus on the intent of the technology and not on the technological capabilities to improve outcomes.”
2019 Mobile world Congress Featured Content from Mobile world Live
SOME LINKS WORTH CHECKING OUT
- IoT Trends To Drive Innovation For Business In 2019-2020
- IT Execs See Promise In IoT, Reinforcing Microsoft’s $5B Investment
- Internet of Things (IoT) in healthcare: benefits, use cases and evolutions
- Next big things in IoT predictions for 2020
- 68% of businesses are struggling to hire talent for IoT
- So You Want A Job In IoT? Here Are The Three Skills Every IoT Company Looks For.
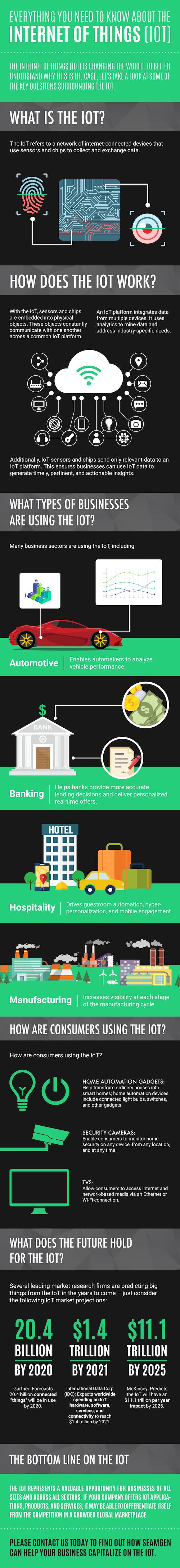
The following infographic is the work of SEAMGEN
Everything you need to know about the Internet Of Things (IoT): Infographic